Unraveling the History of Normal Distribution: From Origins to Modern Applications in Statistical Analysis and Inference.
Introduction
The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution or the bell curve, is a fundamental concept in statistics and probability theory. It is widely used in various fields, from social sciences to natural sciences, economics, engineering, and more. This blog post aims to explore the fascinating history of the normal distribution, tracing its origins, development, and its importance in modern statistical analysis.
Origins of the Normal Distribution
The origins of the normal distribution can be traced back to the 18th century when mathematicians and scientists began studying the concept of errors in measurements. In 1733, the English mathematician Abraham de Moivre introduced the concept of the normal curve, describing the distribution of errors in repeated measurements. However, it was the work of the renowned French mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace that laid the foundation for the modern understanding of the normal distribution.
Laplace and the Central Limit Theorem
Pierre-Simon Laplace, often referred to as the “French Newton,” made significant contributions to probability theory. In his work, Laplace established the Central Limit Theorem, which states that the sum or average of a large number of independent and identically distributed random variables tends to follow a normal distribution, regardless of the shape of the original distribution.
Gauss and the Bell Curve
While Laplace played a crucial role in establishing the theoretical foundation of the normal distribution, it was the German mathematician and astronomer Carl Friedrich Gauss who popularized its practical applications. Gauss introduced the concept of the bell curve, which describes a symmetrical distribution with a peak at the mean value. His work revolutionized the field of statistics and made the normal distribution an essential tool for analyzing data.
Development of Statistical Theory
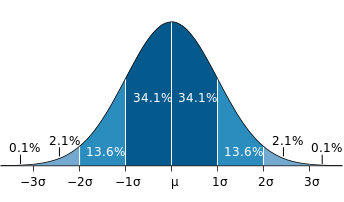
In the 19th and 20th centuries, statisticians and mathematicians further developed the theory behind the normal distribution. Notable contributions were made by mathematicians such as Adolphe Quetelet, Francis Galton, and Karl Pearson. They expanded the understanding of the normal distribution’s properties, including its mean, standard deviation, and the empirical rule that states that approximately 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations.
Applications of the Normal Distribution
The normal distribution finds extensive applications in various fields. In social sciences, it is used to model human characteristics such as height, weight, and IQ scores. In natural sciences, the normal distribution is utilized to describe phenomena such as particle velocities, temperature measurements, and errors in experimental data. In finance, the normal distribution is a fundamental assumption in many financial models, including the widely used Black-Scholes option pricing model.
Statistical Inference and Hypothesis Testing
The normal distribution plays a vital role in statistical inference and hypothesis testing. Many statistical tests, such as the t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and regression analysis, rely on the assumption of normality. These tests enable researchers to draw conclusions about populations based on sample data and make informed decisions.
Modern Developments and Extensions
In recent years, advancements in statistical theory have expanded the understanding and applications of the normal distribution. Variations of the normal distribution, such as the multivariate normal distribution and the skewed normal distribution, have been developed to accommodate complex data patterns. Additionally, advancements in computational techniques have made it possible to analyze large datasets and perform simulations, enhancing the practicality and power of the normal distribution in data analysis.
Summary
The history of the normal distribution is a journey that spans centuries and involves the contributions of many brilliant minds. From its origins in error analysis to its widespread use in various disciplines, the normal distribution has become a cornerstone of statistical theory and practice. Its versatility, simplicity, and robust mathematical properties make it an indispensable tool for data analysis, inference, and decision-making. Understanding the history and significance of the normal distribution provides valuable insights into the foundations of modern statistics and the power of this fundamental concept.
